Earth remote sensing
Satellites for Earth remote sensing are taking photos of the Earth’s surface in visible and infrared ranges (picture 1):
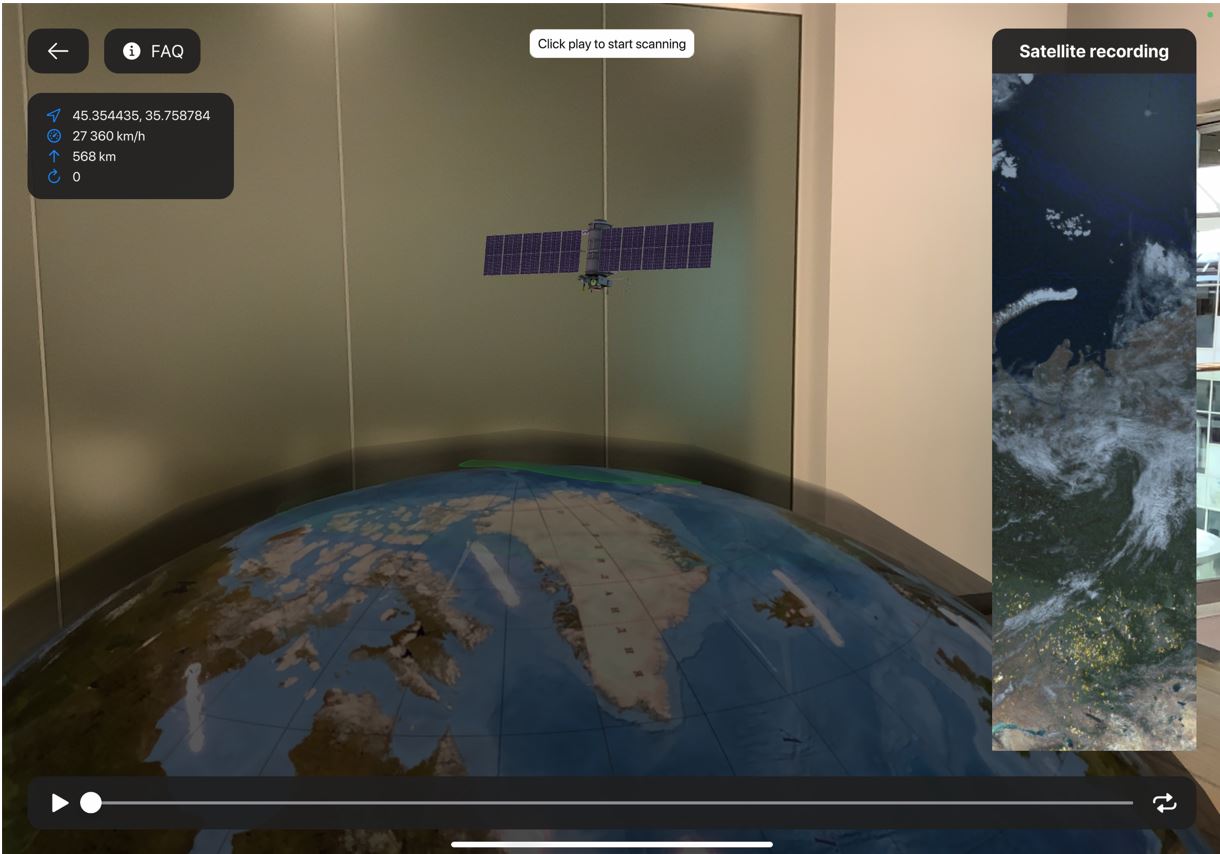
Picture 1. Model of ERS satellite in augmented reality
Spacecrafts of ERS could be on the geostationary orbit (35786 km above sea level), and it’s always watching one and the same plot of the surface, or it could be on the Low Earth Orbit (400-900 km), and it could get an image of most of the planet.
When you launch this unit, you can see how the spacecraft scanning the Earth surface. In Satellite recording widget you can see the surface scanned by the ERS satellite (picture 2):
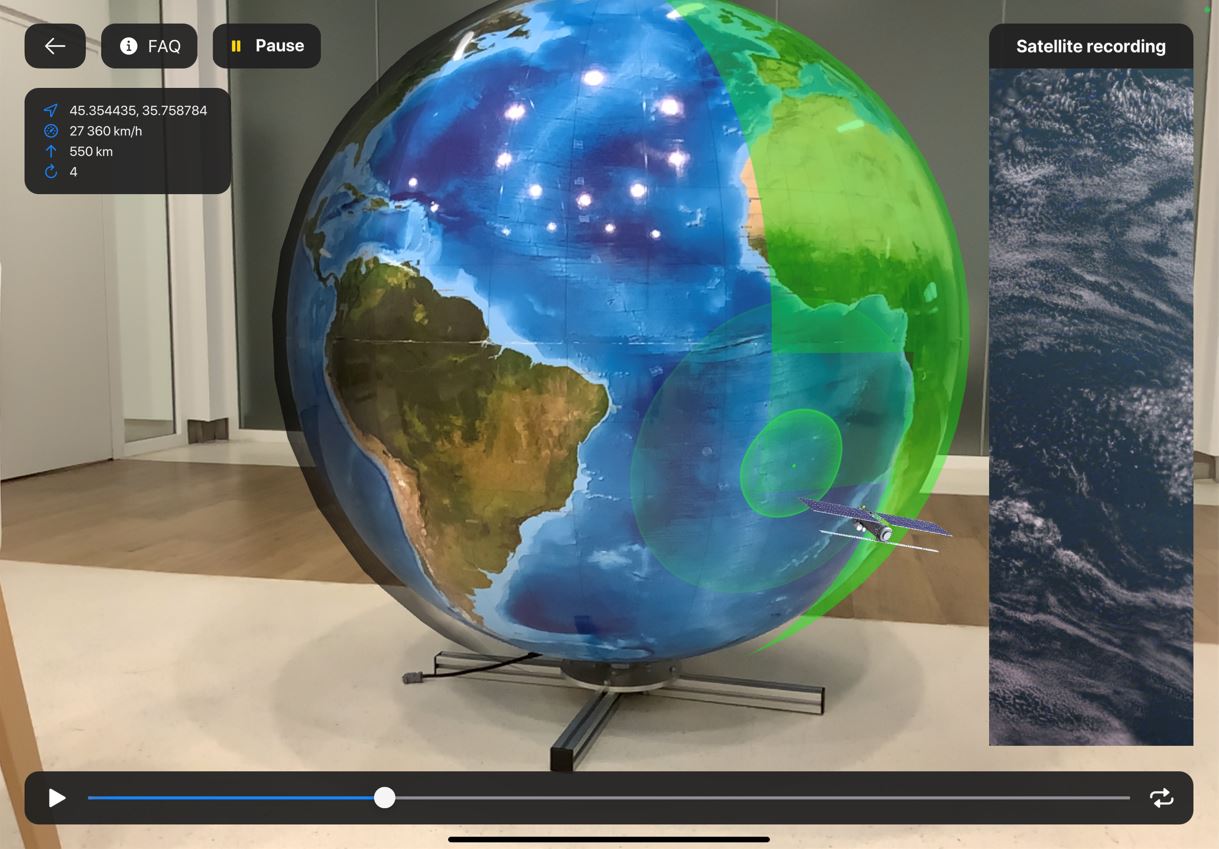
Picture 2. Scanning surface of Earth with ERS satellite
You can see on the picture of this example the spacecraft on the polar orbit. Such type of the spacecraft could get an image of any part of the surface, including the polar areas (picture 3):
Picture 3. Scanning with the satellite on the polar orbit
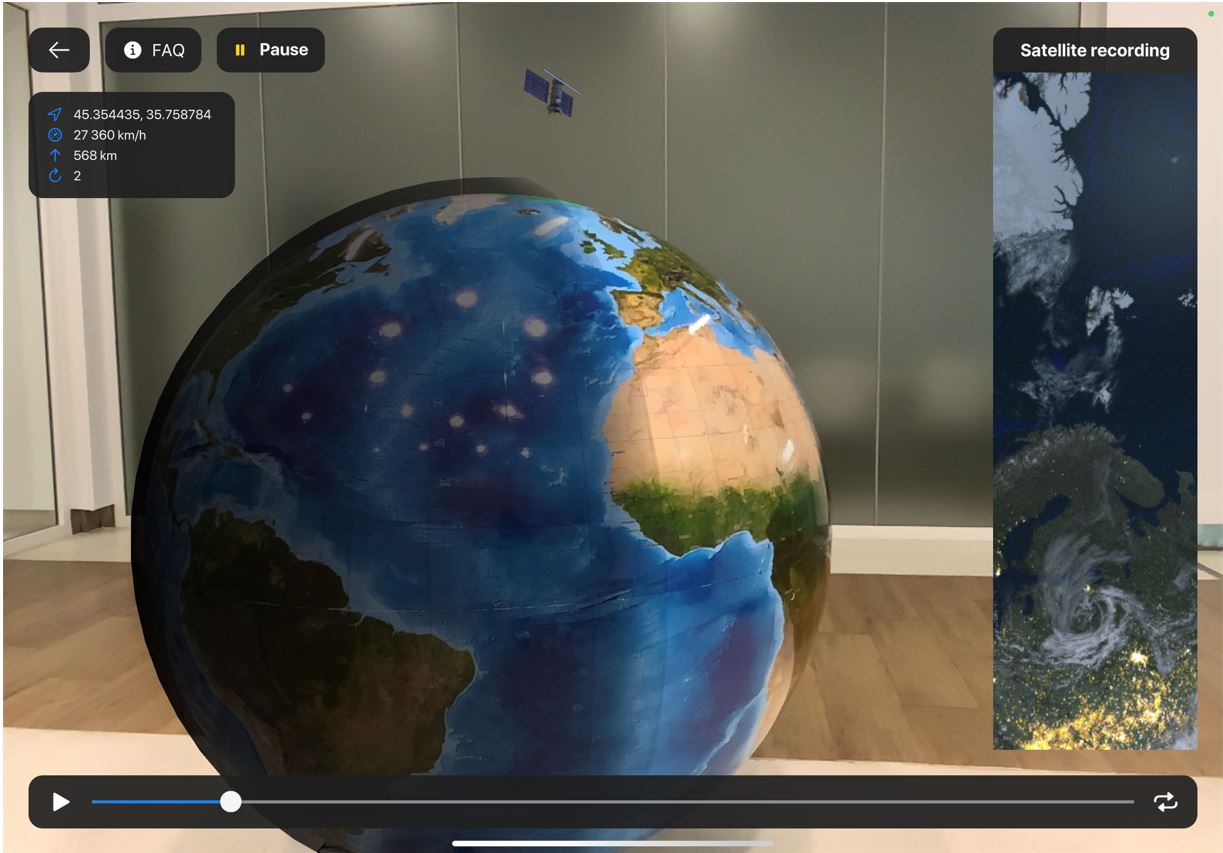
You can see in this visualization that the spacecraft is flying out of Earth’s sync and could take photos of the dayside and the nightside. The real spacecraft “Meteor-M” №2 is flying on the sun-synchronous orbit and always close to the separating line of the day and the night (terminator). Meanwhile he Sun is illuminating all the objects on the side and they are more visible on the photos.