Orbits of weather satellites
Information about the weather satellites
The launch date of Meteor-M 2 – July 8, 2014 (picture 1):
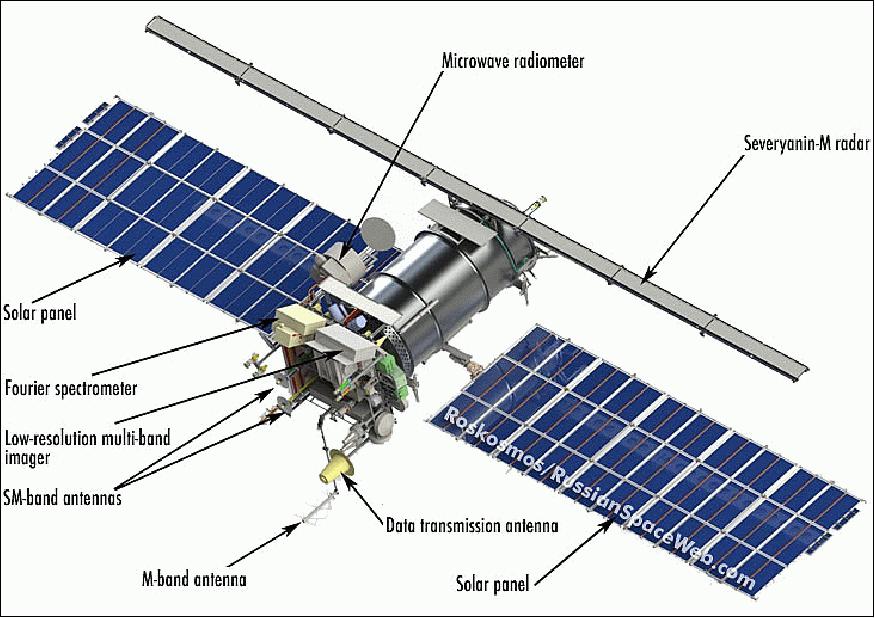
Picture 1. Meteor-M 2
Function of the satellite
The Global Atmosphere Watch and the underlying surface of the Earth, which allows systematically get hydrometeorological and heliogeophysical information on a planetary scale.
Tasks
- The global watch over the underlying surface of the Earth;
- Environmental monitoring;
- Emergency monitoring of natural and technogenic character;
- Agriculture and forestry tasks;
- Scientific research;
- Collecting and transmitting data of different types of data-collection platform (ground, ice and drifting).
Visualization of the weather satellite’s flight in AR mode
You can find an information about visualization of the weather satellite in AR mode at this page
The main features
- The orbit is circle sun-synchronous, Нср=832 км,Т=101,3 мин, i=98,85º;
- Energy supply: the average daily till 1000 w, maximum during 10 minutes – till 1350 w;
- The active life: 7 years;
- The weight: 2700 kg;
- The weight of the payload: 320 kg.
The basic complect of information technology equipment
- Multispectral optical devices in the visible and infrared range (КМСС, МСУ-МР);
- Radiometric equipment of SHF range for humidity and temperature remote sensing of the atmosphere (МТВЗА-ГЯ) - SHF radiometer;
- Infrared Fourier Transform for humidity and temperature remote sensing (ИКФС-2) – for the spacecraft “Meteor-M” №2;
- Heliogeophysical hardware complex, collecting five devices at one platform for learning wide spectrum radio energy;
- On-board radiolocation system for getting radiolocation images of the Earth’s surface despite the weather;
- Radio engineering complex of collecting and transmitting data, including data receiving system from ground-based measuring platforms;
- Basic technical characteristics of spacecraft “Meteor-M” onboard equipment.
Low-resolution multichannel scanning device:
Spectral range of filming, mkm:
- Red (0,5 ÷ 0,7);
- Near-infrared (0,7 ÷ 1,1);
- Medial-infrared (1,6 ÷ 1,8);
- Medial-infrared (3,5 ÷ 4,1);
- Far-infrared (10,5 ÷ 11,1);
- Far-infrared (11,5 ÷ 12,5).
Capture band (shooting from the orbit 835 km) – 2800. Spatial resolution (the size of pixel’s projection on the Earth with H=835 km) - < 1,0 km
Multizone spectral survey complex:
The number of spectral channels – 3.
Spectral range of filming, mkm:
- Green;
- Red;
- Near infrared.
The field of vision two cameras, working at the same time is 900 km, the camera resolution – 60-120 m.
On-board radiolocation complex:
Carrier frequency of the probing signal – 9500-9700 MHz
Bandwidth of shooting – not less than 600 km
Spatial resolution:
- Low resolution mode – 0,7×1,0 km;
- Medium resolution mode – 0,4×0,5 km.
Microwave scanner for temperature and humidity sounding of the atmosphere:
- The number of channels – 29;
- Spectral range - 10,6 ÷ 183,31HHz;
- Swath – 1500 km;
- Spatial resolution – 16-198 km.
Data collection and transmission system:
- Number of platforms served – till 5 thousand;
- Number of simultaneously served platforms – till 150.
You can find NODAR ID of the meteorological satellites with Gpredict Software here - Searching satellites for AR visualization
Visualization of the weather satellite’s orbit in AR
Add the satellite Meteor-M2 by the NORAD ID 40069 (picture 2):

Picture 2. Meteor-M2 weather satellite
This satellite is on the sun-synchronous orbit (picture 3):

Picture 3. Orbit of the weather satellite
Satellites on the sun-synchronous orbit pass over the Earth’s surface almost at one and the same solar time. The illumination angle of the Earth’s surface will be almost the same at all passes of the satellite. Constant conditions of illumination are very great for satellites’ which are getting images of the Earth’s surface (including satellites of Earth remote sensing, weather satellites).