08 Lesson. Getting to know solar sensors
Getting to know the smartphone's light sensor
Install the Andro sensor application or a similar application in your smartphone with information output from the built-in sensors of your smartphone. Launch the app and find the light sensor called LIGHT.
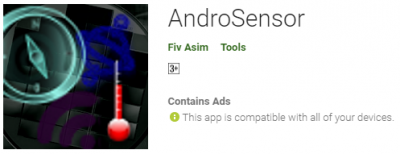
Picture 1. The Andro sensor app
The illumination varies in lux, one lux is equal to the illumination of a surface area of 1 m2 with a luminous flux of radiation incident on it equal to 1 lumen. Accordingly, the following will be performed: 1 lux = 1 lm/m2.
Picture 2. Illumination
One lumen is equal to the luminous flux emitted by a point source with a luminous intensity equal to one candela, at a solid angle of one steradian.
Picture 3. Lumen
The total luminous flux generated by a point source, with a luminous intensity of one candela, is equal to 4π lumens. Candela is the power of light, the energy strength of which is 1/683 W/steradian. The intensity of the light emitted by a paraffin candle is close to one candela.
Picture 4. Paraffin candle
Lighting requirements in workplaces equipped with personal computers according to the SanPiN 2.2.2/2.4.1340-03 : Illumination on the desktop: 300-500 lux. Illumination on the PC screen: not higher than 300lk.
Checking the operability of solar sensors
Connect the BKU to the PSS and four solar sensors. Download the following program to the BKU, which will output the values read from the solar sensors.
Python code:
def control(): # The main function of the program in which to call the rest of the functions
sun_result = [0,0,0] # Initialize sun_result
num = 1
print "Enable sun sensor №", num
sun_sensor_turn_on(num)
sleep(1)
print "Get RAW data from sun sensor"
for i in range(10):
sun_result = sun_sensor_request_raw(num)
if not sun_result[0]: # if the sensor returned an error message,
print "state:", sun_result[0], "raw =", sun_result[1], \
sun_result[2]
elif sun_result[0] == 1:
print "Fail because of access error, check the connection"
elif sun_result[0] == 2:
print "Fail because of interface error, check your code"
sleep(1)
print "Disable sun sensor №", num
sun_sensor_turn_off(num)
Code in C:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "libschsat.h"
#define LSS_OK 0
#define LSS_ERROR 1
#define LSS_BREAK 2
int control(){ //The main function of the program
uint16_t sun_result[] = {0, 0, 0}; // initialize sun_result
uint16_t num = 1; // number of the solar sensor
printf("Enable sun sensor №%d\n", num);
sun_sensor_turn_on(num); //turning on the sensor
Sleep(1); //Waiting for 1 second
to turn on printf("Get RAW data from sun sensor #%d\n", num);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) //reading the display 10 times
{
sun_result[0] = sun_sensor_request_raw(num,& sun_result[1],& sun_result[2]);/*check how it works, it's very strange what works
if it doesn't set sun_result[0] */
if(!sun_result[0]){ //if the sensor did not return an error message,
printf("state: %d raw = %d, %d\n", i, sun_result[1], sun_result[2]);
}
else if (sun_result[0] == 1) { // if the sensor returned an error message 1
printf("Fail because of access error, check the connection\n");
}
else if (sun_result[0] == 2) { // if the sensor returned an error message 2
printf("Fail because of interface error, check you code\n");
}
Sleep(1); //readings are read once per second
}
printf("Disable sun sensor no.%d\n", num);
sun_sensor_turn_off(num); //turning off the solar sensor
return 0;
}
Run the program, with room lighting, the sensor values will be in the range from 70 to 300. Direct the light from the sun simulator at the sensors – now the values will vary from 70 to 20,000.
Collecting values for calibration of solar sensors
Install the AVS Orbicraft and magnetometer on the top panel, and 4 solar sensors on 4 sides of the Orbicraft. Install the solar sensors upside down so that the plumes do not cover the sensor window.

Picture 5. Orbicraft with AVS and magnetometer on the top panel
Download the following program to the BKU.
Код на Python:
время
импорта, математика импорта
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- кодировка: utf-8 -*-
# Коэффициент дифференциальной обратной связи.
# Коэффициент подбирается экспериментально в зависимости от формы
# и массы вашего спутника.
кд = 200,0
# Временной шаг работы алгоритма,
s time_step = 0.05
# Целевая угловая скорость спутника, град/с.
# Для режима стабилизации равна 0.0.
омега-цель = 0,0
# Максимально допустимая скорость маховика, об/мин
mtr_max_speed = 5000
# Номер маховика
mtr_num = 1
# Номер AVS (датчик угловой скорости)
номер года = 1
# Номер магнитометра
максимальное значение = 1
# Номер результата измерений
i = 1
# Угол поворота текущий
альфа = 0,0
# Функция включает все приборы,
# которые будут использоваться в основной программе.
def initialize_all():
выведите "Включить датчик угловой скорости №", номер поворота по часовой
стрелке(номер поворота по часовой стрелке)
режим ожидания(1)
выведите команду "Включить магнитометр", значение параметра
magnetometer_turn_on(mag_num)
режим ожидания(1) # Ждем включения 1 секунду
напечатайте "Включить солнечные датчики 1-4".
sun_sensor_turn_on(1)
sun_sensor_turn_on(2)
sun_sensor_turn_on(3)
sun_sensor_turn_on(4)
сон(1)
выведите "Включить двигатель №", mtr_num
режим двигателя_отключения(mtr_num)
режим ожидания(1)
# Функция отключает все приборы,
# которые будут использоваться в основной программе.
def switch_off_all():
выведите "Завершение..."
значение скорости поворота (номер скорости)
значение скорости поворота магнитометра (номер магнетрона)
sun_sensor_turn_off(1)
sun_sensor_turn_off(2)
sun_sensor_turn_off(3)
sun_sensor_turn_off(4)
установленная скорость двигателя(mtr_num, 0)
режим ожидания(1)
motor_turn_off(mtr_num)
вывести "Завершить программу"
def mag_calibrated(magx,magy,magz):
# вместо этих 3-х строк кода с коэффициентами калибровки, должны быть строки с коэффициентами калибровки для Вашего магнитометра
#magx_cal = 1,04*magx - 0,26*magy + 0,05*magz - 68,76 # это 1-я строчка, которую необходимо зафиксировать для анализа калорийности в Большом магниетометре
#магі_кал = 0,24*магіх + 1,04*магіх + 0,29*магз + 256,92 # это 2-я строчка, которую необходимо запомнить для анализа калорийности в Большом магниетометре
#magz_cal = -0,09*magx - 0,19*magy + 0,77*magz + 159,41 # это 3-я строчка, которую необходимо запомнить для анализа калорийности в Большом магниетометре
magx_cal = 1,06*(magx + -7,49) + -0,01*(magy + -23,59) + 0,07*(magz + -108,24)
magy_cal = -0,01*(magx + -7,49) + 1,11*(magy + -23,59) + 0,09*(magz + -108,24)
магз_кал = 0,07*(магз + -7,49) + 0,09*(магз + -23,59) + 1,00*(магз + -108,24)
возвращает значения magx_cal, magy_cal, magz_cal
# Функции для определение новой скорости маховика.
# Новая скорость маховика складывается из
# текущей скорости маховика и приращения скорости.
# Приращение скорости пропорционально ошибке по углу
# и ошибке по угловой скорости.
# mtr_speed - текучая скорость, об/мин
# омега - текучая среда, город/с
# омега_цель - главная цель спутника, город/с
# mtr_new_speed - огромная скорость, об/мин
def motor_new_speed_PD(mtr_speed, omega, omega_goal):
mtr_new_speed = int(mtr_speed
+ kd*(омега-омега_цель)
)
если mtr_new_speed > mtr_max_speed:
mtr_new_speed =
mtr_max_speed, если mtr_new_speed < -mtr_max_speed:
mtr_new_speed = -mtr_max_speed
возвращает mtr_new_speed
# Основная функция программы, в которой вызываются остальные функции.
def control():
omega_goal = 0 # omega_goal - главная цель спутника, град/с
инициализируй_ все()
# Инициализируем статус маховика
mtr_state = 0
# Анализируем статистику АВС
hyro_state = 0
sun_sensor_num = 0 # Анализируем изменения для номера отдельного датчика
sun_result_1 = [0,0,0] # Анализируем sun_result_1
sun_result_2 = [0,0,0] # Анализируем sun_result_2
sun_result_3 = [0,0,0] # Анализируем sun_result_3
sun_result_4 = [0,0,0] # Анализируем sun_result_4
mag_alpha = 0
вывод_дата_все = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
вывод_данных = [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
# Номер результата измерений
i = 0
# Запоминаем время начала вращения
time_start = время.time()
# Запоминаем время начала секундного интервала
time_interval = time.время()
# Интервал вывода данных с солнечных датчиков в секундах
time_output = 0.1
при значении True:
# Опрос датчика угловой скорости и маховика.
значение параметра hyro_state, gx_raw, gy_raw, gz_raw = значение параметра hyro_request_raw(номер параметра)
mtr_state, mtr_speed = скорость движения двигателя(mtr_num)
mag_state, magx_raw, magy_raw, magz_raw = magnetometer_request_raw(mag_num)
# Работа с указанным датчиком угловой скорости,
# повышение угловой скорости оператора по указанию AVS.
# Если бы хибки были равны 0, т.е. хибки нет
если бы не хиро_государство:
gx_degs = gx_raw * 0,00875
gy_degs = gy_raw * 0,00875
gz_degs = gz_raw * 0,00875
# если бы я был уверен, что я здесь, то это была бы большая честь
# девушка советует с просьбой ПОМОЧЬ мне, именно
# невозможно изменить знак: омега = - gz_degs
омега = gz_degs
elif hyro_state == 1:
выведите "Сбой из-за ошибки доступа, проверьте подключение"
elif hyro_state == 2:
выведите "Сбой из-за ошибки интерфейса, проверьте свой код"
#Обработка показаний маховика и установка трубемой угловой скорости.
если нет, то mtr_state: # были бы цифры 0, т.е. цифры нет
# установка новой скорости маховика
mtr_new_speed = Скорость двигателя_new_speed_pd(mtr_speed,omega,omega_goal)
скорость двигателя_установки_speed(mtr_num, mtr_new_speed)
time.sleep(временный_шаг)
time_current = time.time() - время
начала, если нет значения mag_state: # если значение вернуло код ohibki 0, т.е. ohibki нет
magx_cal, magy_cal, magz_cal = маг_калиброванный(magx_raw,magy_raw,magz_raw)
magy_cal = - magy_cal # перейдем из левой системы координат, которая представляет собой магнитометр во главе, для того, что бы вы могли использовать это приложение было способствовать часовой стрельбе
mag_alpha = math.atan2(магия_кал, магх_кал)/математическое число пи*180
если (время.время() - интервал времени) > time_output:
# Запоминаем время начала следующего секундного интервала
time_interval = time.время()
sun_result_1 = sun_sensor_request_raw(1)
sun_result_2 = sun_sensor_request_raw(2)
sun_result_3 = sun_sensor_request_raw(3)
sun_result_4 = sun_sensor_request_raw(4)
#вывести sun_result_1, sun_result_2, sun_result_3, sun_result_4, mag_alpha, time_current
выходные данные = [time_current, sun_result_1[1], sun_result_1[2], sun_result_2[1], sun_result_2[2], sun_result_3[1], sun_result_3[2], sun_result_4[1], sun_result_4[2], mag_alpha]
output_data_all += вывод_данных
если я > 100: # Начинаем изменение через 5 лет после запуска
omega_goal = 6.0 # omega_goal - главная цель спутника, град/с
если time_current > 90:
перерыв
i += 1
switch_off_all()
выведите "time_end = " , time.time() - время начала
для i в диапазоне(0, 5000, 10):
напечатайте output_data_all[i-1], output_data_all[i], output_data_all[i+1], output_data_all[i+2], output_data_all[i+3], output_data_all[i+4], output_data_all[i+5], output_data_all[i+6], output_data_all[i+7], вывод_дата_все[i+8]
Code in C:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include "libschsat.h"
#define LSS_OK 0
#define LSS_ERROR 1
#define LSS_BREAK 2
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
/*Differential feedback coefficient.
The coefficient is positive if the flywheel is positioned with the z axis up
and the AVS is positioned with the z axis also up.
The coefficient is selected experimentally depending on the shape
and mass of your satellite.*/
const float kd = 200.0;
// The time step of the algorithm, with
const float time_step = 0.1;
/* Target angular velocity of the satellite, deg/s. For stabilization mode, it is 0.0.*/
const float omega_goal = 0.0;
// Maximum permissible flywheel speed, rpm
const int mtr_max_speed = 5000;
const uint16_t mtr_num = 1; // Flywheel number
const uint16_t hyr_num = 1; // AVS number
const uint16_t mag_num = 1; // Magnetometer number
// Measurement result number
int i = 1;
// Rotation angle current
const float alpha = 0.0;
void initialize_all(void){/* Function includes all devices,
which will be used in the main program.*/
printf("Enable angular velocity sensor №%d\n", hyr_num);
hyro_turn_on(hyr_num);
Sleep(1);
printf("Enable magnetometer %d\n", mag_num);
magnetometer_turn_on(mag_num);
Sleep(1); // Waiting for 1 second
to turn on printf("Enable Sun sensors 1-4\n");
sun_sensor_turn_on(1);
sun_sensor_turn_on(2);
sun_sensor_turn_on(3);
sun_sensor_turn_on(4);
Sleep(1);
printf("Enable motor №%d\n", mtr_num);
motor_turn_on(mtr_num);
Sleep(1);
}
void switch_off_all(void){/* The function disables all devices
that will be used in the main program.*/
printf("Finishing...");
int16_t new_speed = 0;
hyro_turn_off(hyr_num);
magnetometer_turn_off(mag_num);
sun_sensor_turn_off(1);
sun_sensor_turn_off(2);
sun_sensor_turn_off(3);
sun_sensor_turn_off(4);
motor_set_speed(mtr_num, 0, &new_speed);
Sleep(1);
motor_turn_off(mtr_num);
printf("\nFinish program\n");
}
int mag_calibrated(int16_t *magx, int16_t *magy, int16_t *magz ){
/*The mag_calibrated function corrects
the magnetometer readings taking into account calibration coefficients
instead of these 3 lines of code with calibration coefficients, there should be lines with calibration coefficients for your magnetometer
//magx_cal = 1.04*magx - 0.26*magy + 0.05*magz - 68.76 # this is the 1st line that needs to be replaced based on the results of calibration of your magnetometer
//magy_cal = 0.24*magx + 1.04*magy + 0.29*magz + 256.92 # this is the 2nd line to be replaced based on the results of calibration of your magnetometer
//magz_cal = -0.09*magx - 0.19*magy + 0.77*magz + 159.41 # this is the 3rd line to be replaced based on the results of calibration of your magnetometer*/
float magx_cal;
float magy_cal;
float magz_cal;
magx_cal = 1.06*(*magx + -7.49) + -0.01*(*magy + -23.59) + 0.07*(*magz + -108.24);
magy_cal = -0.01*(*magx + -7.49) + 1.11*(*magy + -23.59) + 0.09*(*magz + -108.24);
magz_cal = 0.07*(*magx + -7.49) + 0.09*(*magy + -23.59) + 1.00*(*magz + -108.24);
*magx = magx_cal;
*magy = magy_cal;
*magz = magz_cal;
return 0;
}
int motor_new_speed_PD(int mtr_speed, float omega, int16_t omega_goal){
/* Function for determining the new flywheel speed.
The new flywheel speed is made up of
the current flywheel speed and the speed increment.
The speed increment is proportional to the angle error and the angular velocity error.
mtr_speed - current angular velocity of the flywheel, rpm
omega - current angular velocity of the satellite, deg/s
omega_goal - target angular velocity of the satellite, deg/s
mtr_new_speed - required angular velocity of the flywheel, rpm*/
int16_t mtr_new_speed;
mtr_new_speed = (int)(mtr_speed + kd * (omega - omega_goal));
if (mtr_new_speed > mtr_max_speed)
{
mtr_new_speed = mtr_max_speed;
}
else if (mtr_new_speed < -mtr_max_speed)
{
mtr_new_speed = -mtr_max_speed;
}
return mtr_new_speed;
}
int control(){// The main function of the program in which the other functions are called.
int16_t omega;
int omega_goal = 0; // omega_goal - target angular velocity of the satellite, deg/s
initialize_all();
int mtr_state = 0; // Initialize the flywheel status
int hyro_state = 0; // Initialize AVS status
int mag_state = 0; // Initialize magnetometer status
int16_t mtr_speed;
int16_t mtr_new_speed;
//AVS
int16_t gx_raw data;
int16_t gy_raw;
int16_t gz_raw;
int16_t *hyrox_raw=&gx_raw;
int16_t *hyroy_raw= &gy_raw;
int16_t *hyroz_raw = &gz_raw;
//magnetometer data
int16_t mgx_cal=0;
int16_t mgy_cal=0;
int16_t mgz_cal=0;
int16_t *magx_raw = &mgx_cal;
int16_t *magy_raw = &mgy_cal;
int16_t *magz_raw = &mgz_cal;
float gx_degs;
float gy_degs;
float gz_degs;
uint16_t sun_result_1[] = {0,0,0}; // Initialize sun_result_1
uint16_t sun_result_2[] = {0,0,0}; // Initialize sun_result_2
uint16_t sun_result_3[] = {0,0,0}; // Initialize sun_result_3
uint16_t sun_result_4[] = {0,0,0}; // Initialize sun_result_4
int mag_alpha = 0;
const int sizeOD = 10;
int sizeODA = 0;
int tempSODA;
// double* output_data = (double*)calloc(sizeOD, sizeof(double));
double* output_data_all = (double*)calloc(sizeODA, sizeof(double));
// Number of the measurement result
int i = 0;
// Remember the start time of rotation
long int time_start = time(NULL);
// Remember the start time of the second interval
long int time_interval = time(NULL);
// Data output interval from solar sensors in seconds
int time_output = 0.1;
int j;
char a=1;
while (a==1){
// Polling the angular velocity sensor and the flywheel.
hyro_state = hyro_request_raw(hyr_num,hyrox_raw,hyroy_raw,hyroz_raw);
mtr_state = motor_request_speed(mtr_num, &mtr_speed);
mag_state = magnetometer_request_raw(mag_num, magx_raw, magy_raw, magz_raw);
if (!hyro_state){
/*Processing angular velocity sensor readings,
calculation of the angular velocity of the satellite based on AVS readings.
If the AVS error code is 0, i.e. there is no error*/
gx_degs = gx_raw * 0.00875;
gy_degs = gy_raw * 0.00875;
gz_degs = gz_raw * 0.00875;
/* if the AVS is set with the z axis up, then the angular velocity
the satellite coincides with the AVS readings along the z axis, otherwise
the sign must be changed: omega = - gz_degs*/
omega = gz_degs;
// printf("gx_degs=%f, gy_degs=%f, gz_degs=%f\n", gx_degs, gy_degs, gz_degs);//just in case
}
else if (hyro_state == 1){
printf("Fail because of access error, check the connection\n");
}
else if (hyro_state == 2) {
printf("Fail because of interface error, check your code\n");
}
//Processing the flywheel readings and setting the required angular velocity.
if (!mtr_state) {// if the error code is 0, i.e. there is no error
int16_t mtr_speed=0;
motor_request_speed(mtr_num, &mtr_speed);
// printf("Motor_speed: %d\n", mtr_speed);
// setting the new flywheel speed
mtr_new_speed = motor_new_speed_PD(mtr_speed,omega,omega_goal);
motor_set_speed(mtr_num, mtr_new_speed, &omega);
}
Sleep(time_step);
long int time_current = time(NULL) - time_start;
if (!mag_state){
mag_calibrated(magx_raw,magy_raw,magz_raw);
*magy_raw = - *magy_raw; /*moving from the left coordinate system,
which is shown on the magnetometer to the right, in order to
the positive direction of the angle was counterclockwise*/
mag_alpha = atan2(mgy_cal, mgx_cal)/M_PI*180;
}
if ((time(NULL) - time_interval) > time_output){
// Memorizing the start time of the next second interval
time_interval = time(NULL);
sun_result_1[0] = sun_sensor_request_raw(1, &sun_result_1[1],&sun_result_1[2]);
sun_result_2[0] = sun_sensor_request_raw(2,&sun_result_2[1],&sun_result_2[2]);
sun_result_3[0] = sun_sensor_request_raw(3,&sun_result_3[1],&sun_result_3[2]);
sun_result_4[0] = sun_sensor_request_raw(4,&sun_result_4[1],&sun_result_4[2]);
int output_data[] = {time_current, sun_result_1[1], sun_result_1[2], sun_result_2[1], sun_result_2[2], sun_result_3[1], sun_result_3[2], sun_result_4[1], sun_result_4[2], mag_alpha};
tempSODA = sizeODA;
sizeODA += sizeOD;
output_data_all = (double*)realloc(output_data_all, sizeODA*sizeof(double));
for (j=tempSODA; j<sizeODA; j++) {
output_data_all[j] = output_data[j-sizeODA+1];
}
}
if (i > 100){ // Starting rotation 5 seconds after launch
omega_goal = 6.0; // omega_goal - target angular velocity of the satellite, deg/s
}
if (time_current > 90){
break;
}
i += 1;
}
switch_off_all();
printf("time_end = %ld" , time(NULL) - time_start);
for (i = 0; i < 5000; i = i + 10){
printf("%f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f, %f\n",output_data_all[i], output_data_all[i+1], output_data_all[i+2], output_data_all[i+3], output_data_all[i+4], output_data_all[i+5], output_data_all[i+6], output_data_all[i+7], output_data_all[i+8], output_data_all[i+9]);
}
printf ("Ok\n");
return 0;
}
According to the results of the program, 500 lines of data with the following type will be output:
onmessage0.132400989532 74 117 27 25 156 214 156 61 -34.6566118491
onmessage0.281419992447 74 116 27 25 156 215 156 61 -34.555539497
onmessage0.438189029694 74 116 27 25 156 214 156 61 -33.6820711721
onmessage0.585952043533 74 116 27 25 156 215 156 61 -34.6566118491
onmessage0.733724832535 74 116 27 25 156 214 156 61 -33.6705914701
onmessage0.88149189949 74 117 27 25 156 214 156 61 -33.7733709383
onmessage1.02926301956 74 117 27 25 156 214 156 61 -33.6745869595
onmessage1.1782848835 74 117 27 25 156 214 156 61 -33.4062495287
onmessage1.32730197906 74 117 27 25 156 214 156 61 -33.2488503276
onmessage1.47507381439 74 117 27 25 156 214 156 61 -33.8923918648
Where the first value is the time since the beginning of measurements, the next two are data from the first solar sensor, the next two values are from the second solar sensor, the next two are from the third and from the fourth. The tenth value is the magnetometer reading (the angle of rotation of the Orbicraft relative to the direction to the magnetic pole). To analyze the received data, copy them from the browser (by selecting with Ctrl-A and copying with Ctrl-C) and save them in a new text document in Notepad++ (paste with (Ctrl-V)). Then you should clear them of the service information at the beginning and at the end of the file. The frequently occurring onmessage service word should be deleted using the Notepad++ replacement function. Press Ctrl-H on the keyboard, type onmessage in the "Find" field, leave the "Replace with" field empty and click on "Replace all" or "Replace in all open documents".
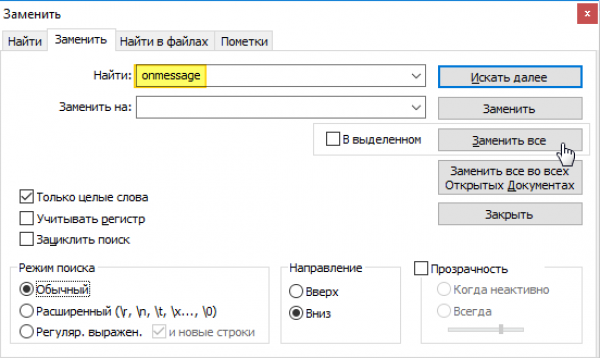
Picture 6. Creating a cleaned up document
Save the cleaned document in a txt file. Now it can be analyzed in Excel.