Ground VHF Transceiver test
The ground transceiver is connected to the computer via USB. It can be tested without turning on OrbiX. The address of the VHF transceiver in hexadecimal format 1F (31 in decimal). List of devices and parameters of the terrestrial VHF transceiver (Picture 1):
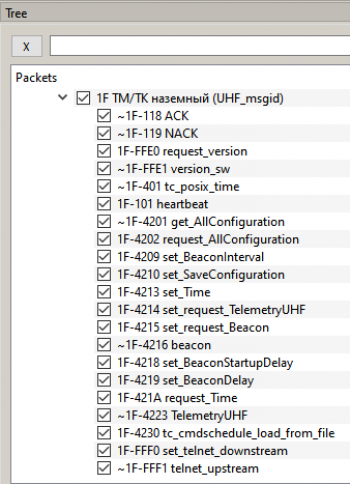
Picture 1. List of ground VHF devices and parameters
Getting the version number
To get the version number, select the command 1F-FFE0 request_version and click on the button To Server (Picture 2):
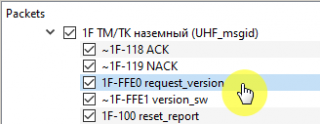
Picture 2. Requesting a version number
This will send the command 1F-FFE0 and return the version number (message ~version_sw) (Picture 3):
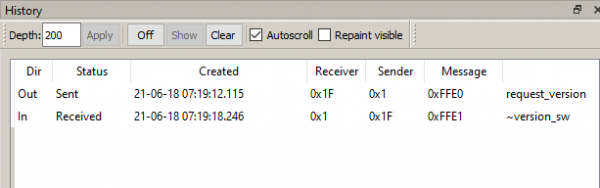
Picture 3. Sending a command
Click on the received message ~version_sw and you can see its fields with the version number (Picture 4):
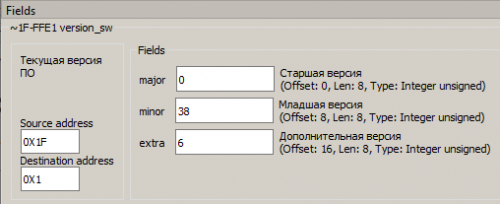
Picture 4. Viewing the version number
Getting the configuration of the VHF transceiver
To get the configuration of the VHF transceiver, select the command 1F-4202 request_AllConfiguration and click on the button To Server (Picture 5):
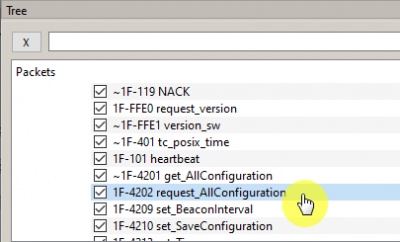
Picture 5. Configuration of the VHF transceiver
This will send the command 1F-4202 and return the configuration (message ~get_AllConfiguration) (Picture 6):
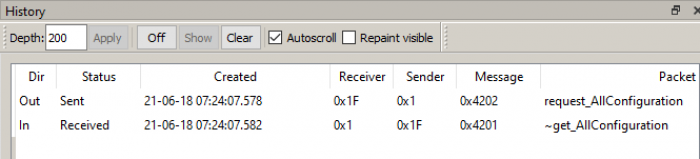
Picture 6. Receiving the configuration message
Click on the received message ~get_AllConfiguration and you can see its fields (Picture 7):
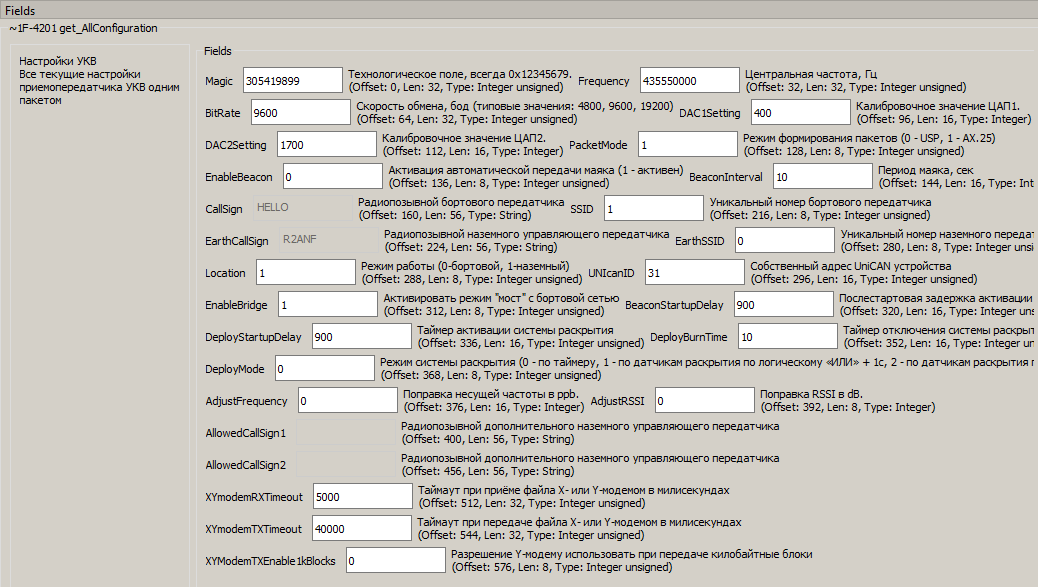
Picture 7. Viewing the configuration
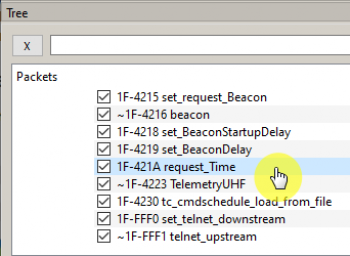
Receiving a VHF transceiver beacon
To receive the beacon (beacon) of the VHF transceiver, select the command 1F-4215 set_request_Beacon and click on the button To Server (Picture 8):
![]()
Picture 8. Selecting the command to receive the VHF beacon
In this case, the command 1F-4215 will be sent and the beacon will be returned (message ~1F-4216 beacon) (Picture 9):
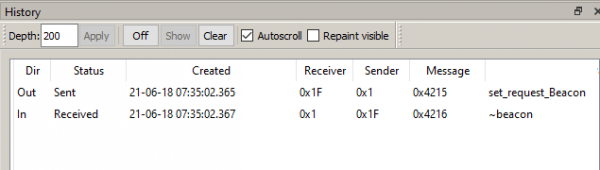
Picture 9. Receiving a message
Click on the received message ~1F-4216 beacon and you can see its fields (Picture 10):
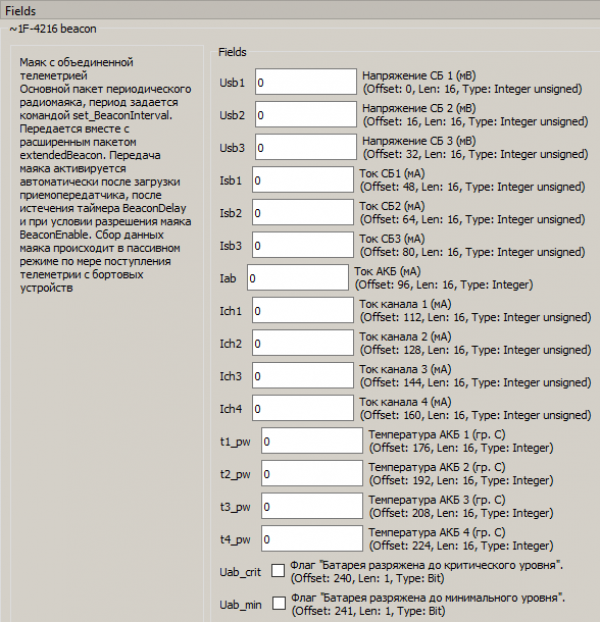
Picture 10. Viewing the received message
Scroll down the message and you will see the following parameters of the VHF transceiver (Picture 11):
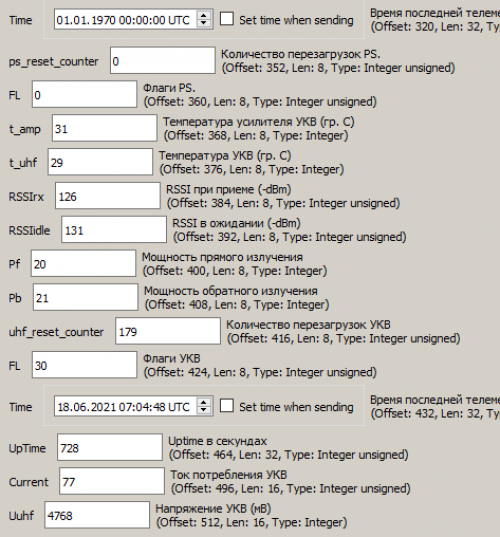
Picture 11. Parameters of the VHF transceiver
- Nres - Number of power-ups (reboots) VHF transceiver;
- Time - The time of the last VHF telemetry in Unix format. 1590775122 is the number of seconds that have passed since midnight on January 1, 1970;
- UpTime - The time elapsed since the VHF transceiver was turned on (rebooted).
Getting the time of the VHF transceiver
To get the time of the VHF transceiver, select the command 1F-421A request_Time and click on the button To Server (Picture 12):
Picture 12. Team Selection
This will send the command 1F-421A and receive a response ~tc_posix_time containing the current time (Picture 13):
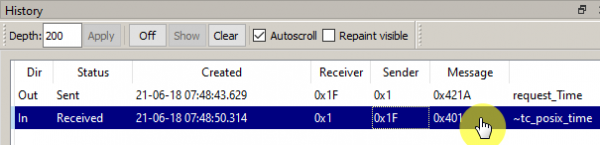
Picture 13. Sending a command
The value of the on-board time can be seen in the Fields field (Picture 14):
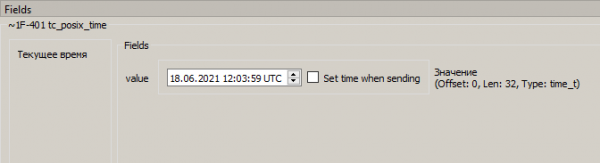
Picture 14. Viewing on-board time
View time in hexadecimal format
Turn on the HexView panel (Picture 15):
Picture 15. Panel Settings
In the HexView panel, you can see the time in hexadecimal format (Picture 16):
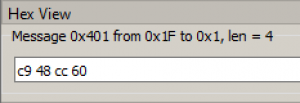
Picture 16. Viewing time in hexadecimal format
However, if we convert the resulting hexadecimal number c9 48 cc 60 to decimal format, we get 3,376,991,328, which is very different from the true Unix time of 1,624,000 713. This is due to the fact that the number c9 48 cc 60 is written in the way "from junior to senior" (English little-endian) as is customary in most modern microprocessors. In this case, the higher digits are written on the right.
In order to correctly convert time to decimal format, it is necessary to rewrite the number as follows: 60 cc 48 c9, which in decimal format is equal to 1,624,000 713. This order of writing numbers, when the highest digits are written on the left (the usual order) is called "from senior to junior" (English big-endian).